Understanding customer issues in real-time is crucial for businesses to improve their products and services, as well as to stay competitive in the market. With the rise of online platforms, it has become easier for customers to voice their complaints and feedback, which can be overwhelming for businesses to keep track of. That's where natural language processing (NLP) comes in. In this blog post, we will explore how businesses can use NLP to understand their own and their competitors' customer issues in real-time. We'll use the case of a fast food market in Europe.
1. Identify sources of customer feedback
The first step in using NLP to understand customer issues is to identify the sources of customer feedback. This could include social media platforms, online reviews, customer support emails and chats, and any other medium through which customers communicate with the business. It is important to gather feedback from a diverse set of sources in order to get a comprehensive understanding of customer issues. In the fast food industry, delivery platforms have become increasingly popular. Customers may face delays in delivery, food may not be as expected, or there could be issues with the delivery service itself.
Sample reviews - in various languages machine-translated into English. Source: Banacha Street.
2. Use NLP to analyze customer feedback
Once the sources of customer feedback have been identified, the next step is to use NLP to analyze this feedback. This involves using algorithms to extract relevant information from the text, such as the specific issues that customers are facing, the sentiment behind their feedback (positive, negative, or neutral), and any other relevant details.
There are a number of tools and platforms that businesses can use to perform this analysis, including transformer-based machine learning techniques.
Sentiment and emotion assessment of sample reviews - BERT model.. Source: Banacha Street.
3. Identify patterns and trends in customer feedback
After the customer feedback has been analyzed, the next step is to identify keywords, patterns and trends in the data. This could involve identifying common issues that are raised by customers, determining the sentiment behind the feedback, and identifying any other trends or patterns that may be relevant to the business.
Keyword detection. Source: Banacha Street.
4. Use the insights to improve products and services
Once the patterns and trends in customer feedback have been identified, businesses can use this information to make improvements to their products and services. This could involve fixing bugs or issues that are commonly reported by customers, improving the overall customer experience, or making other changes based on the insights gained from the customer feedback. For example, if a high number of customers are complaining about long delivery times, the business can use this information to improve their delivery process and communicate with customers about any delays.
5. Monitor competitors' customer issues
In addition to understanding their own customer issues, businesses can also use NLP to monitor the customer issues of their competitors. This can be done by gathering and analyzing customer feedback from the same sources as above, with a focus on the competitor's products and services. This can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the competitor's offerings, as well as potential areas for differentiation. Such data can be used to gain a quick competitive advantage locally. And also dynamically adjust the pricing strategy.
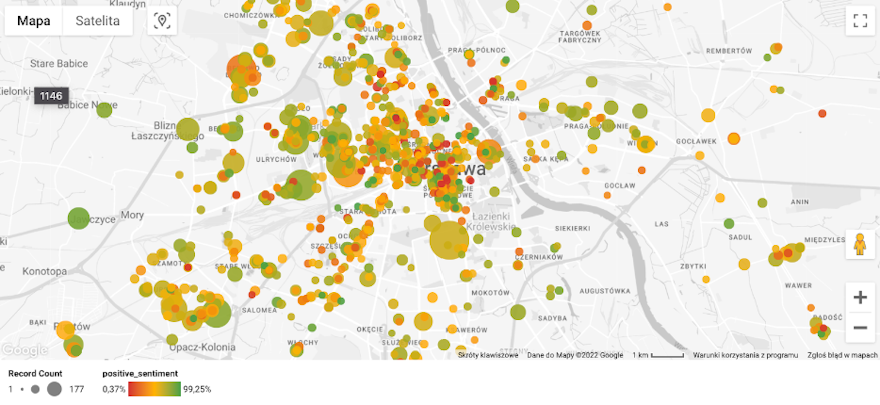
Review sentiment map - restaurants in Warsaw. Source: Banacha Street.
Summary
In conclusion, NLP is a powerful tool for businesses to understand their own and their competitors' customer issues in real-time. By gathering and analyzing customer feedback, businesses can identify patterns and trends, and use this information to make improvements to their products and services. By staying attuned to customer issues, businesses can stay competitive in the market and improve the overall customer experience.
![[object Object]](/lib_gRnApgvCOvsXNYsy/3t99fsmvfqveuvr5.png?w=102)